Adenomyosis
What is adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis occurs when the endometrial tissue, which normally lines the interior of the uterus, exists within and grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. The displaced endometrial tissue continues to act normally meaning, it will get thicker, break down and bleed during each menstrual cycle.
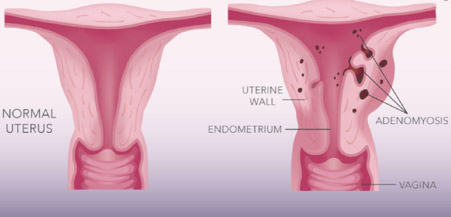
Which are the symptoms?
Sometimes, adenomyosis can be silent, causing no signs or symptoms or only mildly uncomfortable. In other cases, adenomyosis can cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe menstrual cramping (dysmenorrhea) and/or pain during intercourse (dyspareunia). The uterus is usually enlarged.
What is the cause?
The cause remains unknown, but it´s associated with increased levels of estrogen. The disease typically disappears after menopause. It is more frequent after childbearing and uterine surgeries.
What is the treatment?
Adenomyosis is not harmful if it causes no symptoms. For women who experience severe discomfort from adenomyosis, certain medical treatments can help, but hysterectomy (uterus removal) is the only cure.
When to see your doctor?
If you have prolonged, heavy bleeding or severe cramping during your periods that interfere with your daily regular activities. The doctor will perform a gynaecological evaluation and most of the times, a pelvic ultrasound will be needed. Less frequently, an MRI scan will be ordered to obtain high-resolution images of the uterus if they’re unable to make a diagnosis using an ultrasound.
Book your consultation
Consultation in person - X-Clinic
Av. Eng. Duarte Pacheco, nº26 - Piso intermédio 1070-110 Lisboa (in fronte of Amoreiras Shopping)
Consultation in person - Medmulher
Av. Marquês de Tomar 44 1050-162 Lisboa
Online/Video Consultation
Zoom meeting
Contact us:
